Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is the sixth-most-common cancer in the world, and its incidence is increasing. Some three to five males are affected for each female. There are two main types of esophageal cancer—adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer of the esophagus is often detected late inasmuch as there are typically no early symptoms. Nevertheless, if the cancer is caught soon enough, patients can have a five-year survival rate of 90% or above. Diagnosis is by endoscopy biopsy and CT scan.
Surgery involves removal of the esophagus, which can be done by key hole or open surgery , with or without chemotherapy. The stomach or large intestine can be mobilized to the chest cavity to carry out the function of the esophagus
Stomach Cancer
Cancer of the stomach, also called gastric cancer, is the fourth-most-common type of cancer and the second-highest cause of cancer death globally. The most common type of gastric cancer is adenocarcinoma. Important factors that may contribute to the development of gastric cancer include diet, smoking and alcohol consumption, genetic aspects (including a number of heritable syndromes) and infections (for eg, Helicobacter pylori or Epstein-Barr virus) and pernicious anemia. Diagnosis is by endoscopy biopsy and CT scan.
Surgery – The main aim of surgery is removal of the cancer along with a margin of healthy tissue and along with draining lymph nodes, which are sites of earliest spread of cancer. Depending on the amount of stomach that needs to be removed, it may either be a Subtotal Gastrectomy or Total Gastrectomy , with or without chemotherapy. Very early tumours have the option of Endoscopic treatment.
Pancreatic Cancer
This is the fifth-most-common cause of cancer deaths in the United States, and the seventh most common in Europe. These cancers are classified as endocrine or nonendocrine tumors. The most common is ductal adenocarcinoma. The most significant risk factors for pancreatic cancer are advanced age and smoking. Chronic pancreatitis, diabetes or other conditions may also be involved in their development. Early pancreatic cancer does not tend to result in any symptom, but when a tumor is advanced, a patient may experience severe pain in the upper abdomen, possibly radiating to the back. Another symptom might be jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes. Diagnosis is by endoscopy /Endoscopic ultrasound and CT scan
The surgeries performed are:
- Whipple’s procedure – This major surgery is done for cancer involving the head of the pancreas. Here the head of the pancreas along with the adjacent duodenum, lower aspect of bile duct, a portion of stomach and surrounding lymph nodes.
- Distal pancreatectomy - This procedure involves removal of the body and tail for cancer of the body or tail of pancreas.
Liver Cancer
People get liver cancer (also called hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC or hepatoma) typically from a prolonged Hepatitis B or C infection or as a result of cirrhosis from chronic alcoholism. Liver cancer may bring about yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), itching (pruritus), or cause a buildup of fluid in the abdomen (ascites). A person may feel an enlarging mass, or the cancer might be revealed by abnormal liver function tests.
An attending practitioner might order a biopsy, an MRI or a CT scan, and a patient might be monitored through blood tests (including alpha-fetoprotein, liver-function tests or ultrasound. These cancers are typically treated according to their TNM stage and whether or not cirrhosis is present. Options include surgical resection, embolisation, ablation or a liver transplant
Gallbladder Cancer
Cancers of the gallbladder are typically adenocarcinomas, and are common in elderly women. Gallbladder cancer is strongly associated with gallstones, a porcelain gallbladder appearance on ultrasound, and the presence of polyps within the gallbladder. Gallbladder cancer may manifest with weight loss, jaundice, and pain in the upper right of. It is typically diagnosed with ultrasound and staged with CT. Surgery is the only curative option when the cancer is in its very early stage.
Surgery consists of removal of the gallbladder and adjacent liver tissue along with lymph nodes close to the gall bladder. Sometimes a major liver surgery might be needed along with removal of the gallbladder depending upon the stage.
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is a disease of old age: It typically originates in the secretory cells lining the gut, and risk factors include diets low in vegetable fibre and high in fat. If a younger person gets such a cancer, it is often associated with hereditary syndromes like Peutz-Jegher's, hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer or familial adenomatous polyposis.Colorectal cancer can be detected through the bleeding of a polyp, colicky bowel pain, a bowel obstruction or the biopsy of a polyp at a screening colonoscopy. A constant feeling of having to go to the toilet or anemia might also point to this kind of cancer. Use of a colonoscope can find these cancers, and a biopsy can reveal the extent of the involvement of the bowel wall. CT scan is done to stage the disease.
Removal of a section of the colon by key hole surgery is necessary for treatment, with or without chemotherapy. Colorectal cancer has a comparatively good prognosis when detected early.
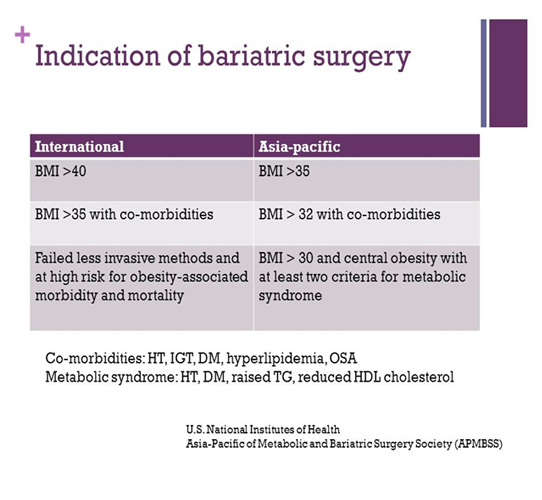
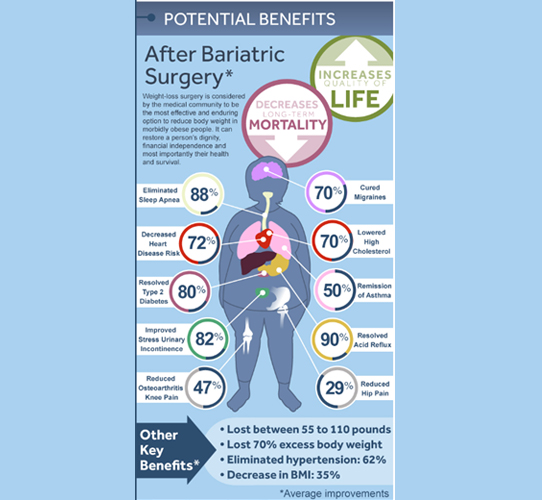
Obesity disorder